Create and use a C++ library on the Mac
This took a little while to figure out. It is a lot of code to write for a simple hello world program, but I learned a few things about macOS along the way.
Create the library
Let's start by creating a hello world library in C++.
mkdir -p HelloLib/{src,build} &&
touch HelloLib/src/{HelloService.hpp,HelloService.cpp} &&
touch HelloLib/CMakeLists.txt
While we're in the shell let's create the target directory for our library, too:
sudo mkdir /opt/hello &&
sudo chown `whoami` /opt/hello
Enter the following into HelloService.hpp:
#ifndef HelloService_hpp
#define HelloService_hpp
#include <string>
class HelloService {
public:
HelloService(const std::string &text);
~HelloService();
public:
void setText(const std::string &text);
const std::string getText();
private:
unsigned int m_count;
std::string m_text;
};
#endif /* HelloService_hpp */
and add the implementation to HelloService.cpp:
#include "HelloService.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
HelloService::HelloService(const string &text) : m_count { 0 }, m_text { text }
{
cout << "HelloService created" << endl;
}
HelloService::~HelloService()
{
cout << "HelloService destroyed" << endl;
}
void HelloService::setText(const std::string &text)
{
m_count = 0;
m_text = text;
}
const std::string HelloService::getText()
{
m_count++;
std::ostringstream oss;
oss << m_text << " " << m_count;
return oss.str();
}
Now let's configure CMake in CMakeLists.txt:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.2)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED ON)
set(CMAKE_CXX_EXTENSIONS OFF)
project(Hello VERSION 0.0.1 DESCRIPTION "HelloService")
add_library(hello SHARED src/HelloService.cpp)
set_target_properties(hello PROPERTIES VERSION ${PROJECT_VERSION})
set_target_properties(hello PROPERTIES PUBLIC_HEADER src/HelloService.hpp)
install(TARGETS hello
LIBRARY DESTINATION ${CMAKE_INSTALL_LIBDIR}
PUBLIC_HEADER DESTINATION ${CMAKE_INSTALL_INCLUDEDIR})
Build and install the library
Now we can build and install the library with the following commands:
cmake -B HelloLib/build -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/opt/hello HelloLib &&
cd HelloLib/build &&
make && make install &&
cd ../..
You should now see the following output for tree /opt/hello:
/opt/hello
include
HelloService.hpp
lib
libhello.0.0.1.dylib
libhello.dylib -> libhello.0.0.1.dylib
Nice. That looks good. Looks like what we wanted, so far. We have the header in /opt/hello/include and the dyamic library in /opt/hello/lib. Let's examine the library with file /opt/hello/lib/libhello.dylib:
/opt/hello/lib/libhello.dylib: Mach-O 64-bit dynamically linked shared library arm64
Perfect.
Let's run one more comand otool -L /opt/hello/lib/libhello.dylib:
/opt/hello/lib/libhello.dylib:
@rpath/libhello.0.0.1.dylib (compatibility version 0.0.0, current version 0.0.1)
/usr/lib/libc++.1.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 904.4.0)
/usr/lib/libSystem.B.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 1292.60.1)
See that the path to libhello.0.0.1.dylib begins with @rpath? This is a cool feature of dyld which we will see later.
Create a CLI program that uses the library
Create a directory:
mkdir -p HelloCLI &&
touch HelloCLI/main.cpp
and enter the following to main.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include "HelloService.hpp"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
HelloService *service = new HelloService("Hi 😎");
cout << service->getText() << endl;
delete service;
return 0;
}
Now compile the program with clang:
clang++ -I /opt/hello/include -L /opt/hello/lib -lhello -rpath /opt/hello/lib -o hello HelloCli/main.cpp
A few words of explanation:
-I /opt/hello/includetells the compiler where to look for the required headerHelloService.hpp.
-L /opt/hello/libtells the linker where it should look for libraries
-lhellotells the linker that it should link againstlibhello.dylib
-rpath /opt/hello/libis the missing puzzle piece. This tells the linker to insert/opt/hello/libinto the Mach-O executable as a runtime path. This allows our library to be found. You can inspect the binary with the following commandotool -l hello:
[...]
Load command 16
cmd LC_RPATH
cmdsize 32
path /opt/hello/lib (offset 12)
[...]
If you run the programm now you should see the following:
HelloService created
Hi 😎 1
HelloService destroyed
Create a Swift program that uses the library
- Create a new Xcode project, choose macOS app, SwiftUI for interface and SwiftUI App for lifecycle.
- Press ⌘-n and begin to type out
Objective-C. Name the fileHelloServiceWrapper - Accept the automatic creation of the bridging header. If you cancelled that you can just create a Header file and name it
<project-name>-bridging-header.h - Create a Header file and name it
HelloServiceWrapper - Rename
HelloServiceWrapper.mtoHelloServiceWrapper.mm
Now from the bridging-header include the wrapper-header:
#include "HelloServiceWrapper.h"
and add the following to HelloServiceWrapper.h:
#ifndef HelloServiceWrapper_h
#define HelloServiceWrapper_h
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface HelloServiceWrapper : NSObject
- (instancetype)initWithText:(NSString*)text;
- (NSString*)getText;
@end
#endif /* HelloServiceWrapper_h */
Here's the implementation of the wrapper class:
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "HelloServiceWrapper.h"
#include "HelloService.hpp"
@interface HelloServiceWrapper()
@property HelloService *service;
@end
@implementation HelloServiceWrapper
- (instancetype)initWithText:(NSString*)text
{
if (self = [super init]) {
self.service = new HelloService(std::string([text cStringUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]));
}
return self;
}
- (NSString*)getText
{
return [NSString stringWithUTF8String:self.service->getText().c_str()];
}
@end
Remeber the long(-ish) command line for clang that we used to compile the CLI tool. We need to tell Xcode the same stuff:
- In build settings add
/opt/hello/includeunder Header Search Paths, and /opt/hello/libraryunder Library Search Paths.- under Other Linker Flags add
-lhello, and-rpath /opt/hello/lib
Now you should be able to compile the project via ⌘-b.
For a simple test enter the following into ContentView.swift:
struct ContentView: View {
private var service: HelloServiceWrapper! = .init(text: "Hallo Welt")
var body: some View {
Text(service.getText())
.padding()
}
}
Hit ⌘-r and voila! 😎 Or not?
Since we have not provided a valid code-signature, yet you need to disable library validation. You can do this under Hardened Runtime -> Disable Library Validation.
Now you should be able to start the program.
Let's replace the library
Navigate to the place inside Derived Data where Xcode has build the binary. The easiest way is to right clock on the App in the Xcode gutter and choose Show in Finder. Double click and you should see something like the following:

Now edit the library code in HelloService.cpp and add something that you can recognise:
diff --git a/src/HelloService.cpp b/src/HelloService.cpp
index 7eeb6ae..74e188a 100644
--- a/src/HelloService.cpp
+++ b/src/HelloService.cpp
@@ -24,6 +24,6 @@ const std::string HelloService::getText()
{
m_count++;
std::ostringstream oss;
- oss << m_text << " " << m_count;
+ oss << m_text << " called: " << m_count << " times.";
return oss.str();
}
and recompile and install the library:
cd HelloLib/build &&
make && make install &&
cd ../..
Without recompiling the app start it again and after you resized it your should see this, now:
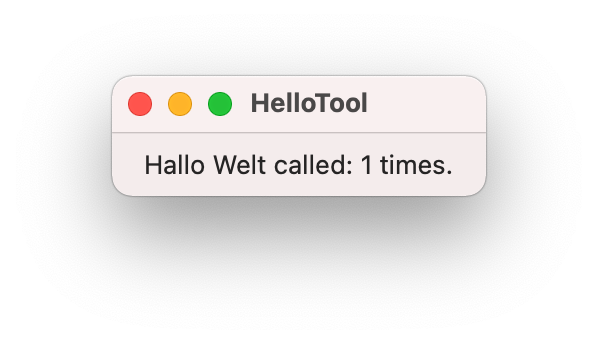
Give it another test. Close the window with ⌘-w and open it again from Finder. Now it should read:
Hallo Welt called: 2 times.
Next?
What do you want to read next? Two things would be cool to figure out:
- How to allow for library validation, and
- How to build an AppKit app only in C++ (I wouldn't consider doing that, but could be fun anyways).
Update
Regarding the missing allowance for library validation. This is how you can codesign directly from CMake. Edit the CMakeLists.txt file:
diff --git a/CMakeLists.txt b/CMakeLists.txt
index 0d2a499..9e37fc4 100644
--- a/CMakeLists.txt
+++ b/CMakeLists.txt
@@ -11,6 +11,8 @@ add_library(hello SHARED src/HelloService.cpp)
set_target_properties(hello PROPERTIES VERSION ${PROJECT_VERSION})
set_target_properties(hello PROPERTIES PUBLIC_HEADER src/HelloService.hpp)
+add_custom_command(TARGET hello POST_BUILD COMMAND codesign -s "your_developer_id_application_certificate" $<TARGET_FILE:hello>)
+
install(TARGETS hello
LIBRARY DESTINATION ${CMAKE_INSTALL_LIBDIR}
PUBLIC_HEADER DESTINATION ${CMAKE_INSTALL_INCLUDEDIR})
Now you can enable library validation in Xcode.